Antiseptics are something that we use almost every day from washing hands to cleaning wounds.
What is Antiseptics?
Antiseptic is a substance or a chemical agent that inhibits the growth and development of microorganisms. They are anti-microbial substances that are applied onto the surface of living tissue to reduce or prevent the chances of infection or sepsis. They are different from antibiotics and disinfectants. Antibiotics are transported inside the body to destroy bacteria within the body and disinfectants destroy microorganisms found on non-living objects whereas antiseptics are used on surface of the body.
Brief History of - Antiseptic
 Joseph Lister came up with the concept of antiseptics. In 1867, he applied Louis Pasteur’s advances in microbiology and came up with the use of carbolic acid as an antiseptic. He used carbolic acid onto the wound of a seven-year-old boy at Glasgow Infirmary, who had sustained a compound fracture. After four days, he changed the pad and discovered that no infection had developed and after a total of six weeks he discovered that the boy's bones had fused back together, without the danger of pus formation.
Joseph Lister came up with the concept of antiseptics. In 1867, he applied Louis Pasteur’s advances in microbiology and came up with the use of carbolic acid as an antiseptic. He used carbolic acid onto the wound of a seven-year-old boy at Glasgow Infirmary, who had sustained a compound fracture. After four days, he changed the pad and discovered that no infection had developed and after a total of six weeks he discovered that the boy's bones had fused back together, without the danger of pus formation.
Usage of Antiseptic
antiseptics is commonly used to reduce the level of microorganisms. They are applied on skin surface and mucous membrane. When skin or mucous membrane is damaged due to various reasons antiseptics are used to disinfect the area and reduce the chance of infection. They are most commonly used for –
- Hand wash
- Pre-operative skin disinfection
- Mucous membrane disinfection
- Preventing and treating infected wounds and burns
- Mouth wash
- Treating mouth and throat infections
Types of Antiseptic
There are different classes of antiseptics classified on the basis of their chemical structure.
Alcohols - Although several alcohols have been shown to be effective antimicrobials, ethyl alcohol (ethanol), isopropyl alcohol and n-propanol are most widely used. They display a broad spectrum of anti-microbial activity against bacteria, viruses and fungi but they are not effevtive against spores.
Biguanides - Chlorhexidine is most widely used in antiseptic products particularly in handwashing and oral products. It is also used disinfectant and preservative. This is due in particular to its broad-spectrum efficacy and low irritation.
Peroxides – hydrogen peroxide is the most common antiseptic used. It is a clear, colorless liquid that is commercially available in a variety of concentrations ranging from 3 to 90%.
Phenol derivates - Chloroxylenol is bactericidal. It is the key halophenol used in antiseptic or disinfectant formulations.
Quaternary Ammonium Compounds - Benzalkonium chloride, Cetrimide are a few QAC’s used. QACs have been used for a variety of clinical purposes like preoperative disinfection of unbroken skin, application to mucous membranes, and disinfection of noncritical surfaces.
Iodine - iodine is rapidly bactericidal, fungicidal, tuberculocidal, virucidal, and sporicidal.
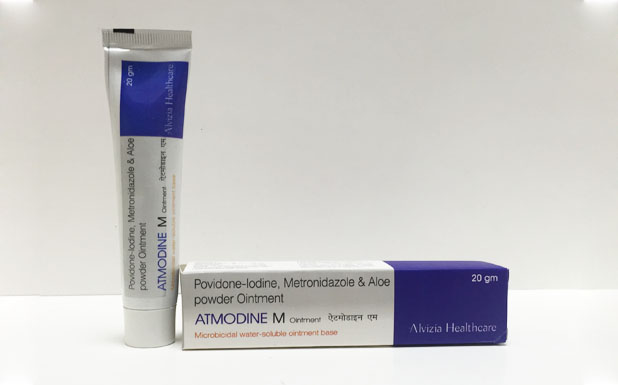
ATMODINE M is an antiseptic cream from Alvizia Healthcare. It contains povidone iodine and metronidazole. Povidone iodine is an organic compound which is less irritating and less toxic.